Condensed matter physics is one of the best examples of emergence. We start with a bunch of small elements which we understand fully at the required level (atoms, electrons, quantum mechanics) but then there are complex properties that show up when we put a bunch of them together.
Includes fun things like:
As of 2020, this is the other "fundamental branch of physics" besides to particle physics/nuclear physics.
Condensed matter is basically chemistry but without reactions: you study a fixed state of matter, not a reaction in which compositions change with time.
Just like in chemistry, you end up getting some very well defined substance properties due to the incredibly large number of atoms.
Just like chemistry, the ultimate goal is to do de-novo computational chemistry to predict those properties.
And just like chemistry, what we can actually is actually very limited in part due to the exponential nature of quantum mechanics.
Also since chemistry involves reactions, chemistry puts a huge focus on liquids and solutions, which is the simplest state of matter to do reactions in.
Condensed matter however can put a lot more emphasis on solids than chemistry, notably because solids are what we generally want in end products, no one likes stuff leaking right?
But it also studies liquids, e.g. notably superfluidity.
One thing condensed matter is particularly obsessed with is the fascinating phenomena of phase transition.
What Is Condensed matter physics? by Erica Calman
. Source. Cute. Overview of the main fields of physics research. Quick mention of his field, quantum wells, but not enough details.AMO is a slightly more general area than condensed matter physics, including related phenomena with smaller numbers atoms and optics. The two terms are however sometimes used as synonyms. The term AMO has gained wide usage and acceptability, see e.g.:
If Ciro had had greater foresight, this might have been what he studied at university!
Molecular beams are cool because they create a one dimensional flow of molecules, which makes it easier to observe certain single-molecule effects, as it removes the multi-particle issues from experiments.
Key molecular beam experiments include:
- Stern-Gerlach experiment, which confirmed the existence of spin
- Rabi's NMR experiment, which confirmed the existence of nuclear spin
The center piece of the control system of atomic clocks is a molecular beam.
Tagged
Bibliography:
Previously on EdX: www.edx.org/learn/quantum-physics-mechanics/delft-university-of-technology-topology-in-condensed-matter-tying-quantum-knots "DelftX: Topology in Condensed Matter: Tying Quantum Knots".
But then they regained their sanity and put the source code on GitHub: github.com/topocm/topocm_content and is CC BY-SA.
How are the bands measured experimentally?
Why are there gaps? Why aren't bands infinite? What determines the width of gaps?
Bibliography:
- Applications of Quantum Mechanics by David Tong (2017) Chapter 2 "Band Structure"
Ciro Santilli distinctly remembers being taught that at basic electrical engineering school during Ciro Santilli's undergrad studies at the University of São Paulo.
It really allows you to do alternating current calculations much as you'd do DC calculations with resistors, quite poweful. It must have been all the rage in the 1950s.
If you adda bit of impurities to certain materials, at low temperatures of a few Kelvin their resistivity actually starts increasing if you go below a certain critical temperature.
Kondo effect graph for gold with added impurities
. Source. The basis of 1970-20XX computers, gotta understand them I guess?
Most notable example: gallium arsenide, see also: gallium arsenide vs silicon.
An important class of semiconductors, e.g. there is a dedicated III-V lab at: École Polytechnique: www.3-5lab.fr/contactus.php
Tagged
Experiments:
- "An introduction to superconductivity" by Alfred Leitner originally published in 1965, source: www.alfredleitner.com/
- Isotope effect on the critical temperature. hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Solids/coop.html mentions that:
If electrical conduction in mercury were purely electronic, there should be no dependence upon the nuclear masses. This dependence of the critical temperature for superconductivity upon isotopic mass was the first direct evidence for interaction between the electrons and the lattice. This supported the BCS Theory of lattice coupling of electron pairs.
20. Fermi gases, BEC-BCS crossover by Wolfgang Ketterle (2014)
Source. Part of the "Atomic and Optical Physics" series, uploaded by MIT OpenCourseWare.Actually goes into the equations.
Notably, youtu.be/O_zjGYvP4Ps?t=3278 describes extremely briefly an experimental setup that more directly observes pair condensation.
Superconductivity and Quantum Mechanics at the Macro-Scale - 1 of 2 by Steven Kivelson (2016)
Source. For the Stanford Institute for Theoretical Physics. Gives a reasonable basis overview, but does not go into the meat of BCS it at the end.The Map of Superconductivity by Domain of Science
. Source. Lacking as usual, but this one is particularly good as the author used to work on the area as he mentions in the video.Lecture notes:
Media:
- Cool CNRS video showing the condensed wave function, and mentioning that "every pair moves at the same speed". To change the speed of one pair, you need to change the speed of all others. That's why there's not energy loss.
Transition into superconductivity can be seen as a phase transition, which happens to be a second-order phase transition.
Tagged
andor.oxinst.com/learning/view/article/measuring-resistance-of-a-superconducting-sample-with-a-dry-cryostat Not a video, but well done, by Oxford Instruments.
Superconductor, 4-probe measurement by Frederiksen Scientific A/S (2015)
Source. OK experiment, illustrates the educational kit they sell. No temperature control, just dumps liquid nitrogen into conductor and watches it drop. But not too bad either. The kit sale link is broken (obviously, enterprise stuff), but there are no archives unfortunately. But it must be some High-temperature superconductorTODO!!! Even this is hard to find! A clean and minimal one! Why! All we can find are shittly levitating YBCO samples in liquid nitrogen! Maybe because liquid helium is expensive?
First 10T Tape Coil by Mark Benz
. Source. Dr. Mark Benz describes the first commercially sold superconducting magnet made by him and colleagues in 1965. The 10 Tesla magnet was made at GE Schenectady and they sold magnets to research facilities world wide before the team formed Intermagnetics General. IGC and Carl Rosner went on to pioneer MRI technology.We know that superfluidity happens more easily in bosons, and so electrons joins in Cooper pairs to form bosons, making a superfluid of Cooper pairs!
Isn't that awesome!
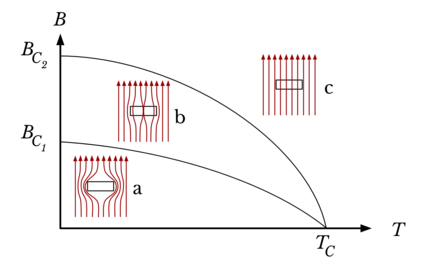
There are various possibilities for the axes, but some common ones:
- temperature (T) vs magnetic field strength (B)
- temperature (T) vs proportion of each chemical element of a binary alloy
- temperature (T) vs pressure
Sketch of the typical superconducting phase diagram of a Type-I superconductor
. Source. Sketch of the typical superconducting phase diagram of a Type-II superconductor
. Source. Sketch of the typical superconducting phase diagram of a Type-I superconductor
. Source. Sketch of the typical superconducting phase diagram of a Type-II superconductor
. Source. As of 2020, basically means "liquid nitrogen temperature", which is much cheaper than liquid helium.
The dream of course being room temperature and pressure superconductor.
Timeline of superconductivity from 1900 to 2015
. Source. Tagged
Upside: superconducting above 92K, which is above the 77K of liquid nitrogen, and therefore much much cheaper to obtain and maintain than liquid helium.
Downside: it is brittle, so how do you make wires out of it? Still, can already be used in certain circuits, e.g. high temperature SQUID devices.
Discovered in 1988, the first high-temperature superconductor which did not contain a rare-earth element.
Superconductivity is one of the key advances of 21st century technology:
- produce powerful magnetic fields with superconducting magnets
- the Josephson effect, applications listed at: Section "Applications of Josephson Junctions"
Tagged
As of 2023 the most important ones economicaly were:The main application is magnetic resonance imaging. Both of these are have to be Liquid helium, i.e. they are not "high-temperature superconductor" which is a pain. One big strength they have is that they are metallic, and therefore can made into wires, which is crucial to be able to make electromagnetic coils out of them.
- Nb-Ti: the most widely used one. Used e.g. to create the magnetic fields of the Large Hadron Collider Up to 15 T.
- Nb-Sn: more expensive than Nb-Ti, but can reach up to 30 T.
TODO, come on, Internet!
Bibliography.
No, see: superconductor I-V curve.
Bibliography:
- physics.stackexchange.com/questions/62664/how-can-ohms-law-be-correct-if-superconductors-have-0-resistivity on Physics Stack Exchange
- physics.stackexchange.com/questions/69222/how-can-i-put-a-permanent-current-into-a-superconducting-loop
- www.quora.com/Do-superconductors-produce-infinite-current-I-V-R-R-0-How-do-they-fit-into-quantum-theory
- www.reddit.com/r/askscience/comments/dcgdf/does_superconductivity_imply_infinite_current/
- www.reddit.com/r/askscience/comments/7xhb46/what_would_happen_if_a_voltage_was_applied_to_a/
Superconducting Short Circuits across Batteries by Eugene Khutoryansky (2020)
Source. Well, internal battery resistance acts as the only resistor, and voltage drops to zero immediately outside of the battery. And you get a huge current.Main theory to explain Type I superconductors very successfully.
TODO can someone please just give the final predictions of BCS, and how they compare to experiments, first of all? Then derive them.
High level concepts:
- the wave functions of pairs of electrons (fermions) get together to form bosons. This is a phase transition effect, thus the specific sudden transition temperature.
- the pairs form a Bose-Einstein condensate
- once this new state is reached, all pairs are somehow entangled into one big wave function, and you so individual lattice imperfections can't move just one single electron off trajectory and make it lose energy
Tagged
Discrete quantum effect observed in superconductors with a small insulating layer, a device known as a Josephson junction.
To understand the behaviour effect, it is important to look at the Josephson equations consider the following Josephson effect regimes separately:
A good summary from Wikipedia by physicist Andrew Whitaker:
at a junction of two superconductors, a current will flow even if there is no drop in voltage; that when there is a voltage drop, the current should oscillate at a frequency related to the drop in voltage; and that there is a dependence on any magnetic field
Bibliography:
- www.youtube.com/watch?v=cnZ6exn2CkE "Superconductivity: Professor Brian Josephson". Several random excerpts from Cambridge people talking about the Josephson effect
Tagged
In 1962 Brian Josephson published his inaugural paper predicting the effect as Section "Possible new effects in superconductive tunnelling".
In 1963 Philip W. Anderson and John M. Rowell published their paper that first observed the effect as Section "Possible new effects in superconductive tunnelling".
Some golden notes can be found at True Genius: The Life and Science of John Bardeen page 224 and around. Philip W. Anderson commented:
As part of the course Anderson had introduced the concept of broken symmetry in superconductors. Josephson "was fascinated by the idea of broken symmetry, and wondered whether there could be any way of observing it experimentally."
The inaugural that predicted the Josephson effect.
Published on Physics Letters, then a new journal, before they split into Physics Letters A and Physics Letters B. True Genius: The Life and Science of John Bardeen mentions that this choice was made rather than the more prestigious Physical Review Letters because they were not yet so confident about the results.
Paper by Philip W. Anderson and John M. Rowell that first (?) experimentally observed the Josephson effect.
Paywalled by the American Physical Society as of 2023 at: journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.10.230
TODO understand the graphs in detail.
They used tin-oxide-lead tunnel at 1.5 K. TODO oxide of what? Why two different metals? They say that both films are 200 nm thick, so maybe it is:
-----+------+------+-----
... Sn | SnO2 | PbO2 | Pb ...
-----+------+------------
100nm 100nmA reconstruction of their circuit in Ciro's ASCII art circuit diagram notation TODO:
DC---R_10---X---GThere are not details of the physical construction of course. Reproducibility lol.
This is what happens when you apply a DC voltage across a Josephson junction.
It is called "AC effect" because when we apply a DC voltage, it produces an alternating current on the device.
By looking at the Josephson equations, we see that a positive constant, then just increases linearly without bound.
Therefore, from the first equation:we see that the current will just vary sinusoidally between .
This meas that we can use a Josephson junction as a perfect voltage to frequency converter.
Wikipedia mentions that this frequency is , so it is very very high, so we are not able to view individual points of the sine curve separately with our instruments.
Also it is likely not going to be very useful for many practical applications in this mode.
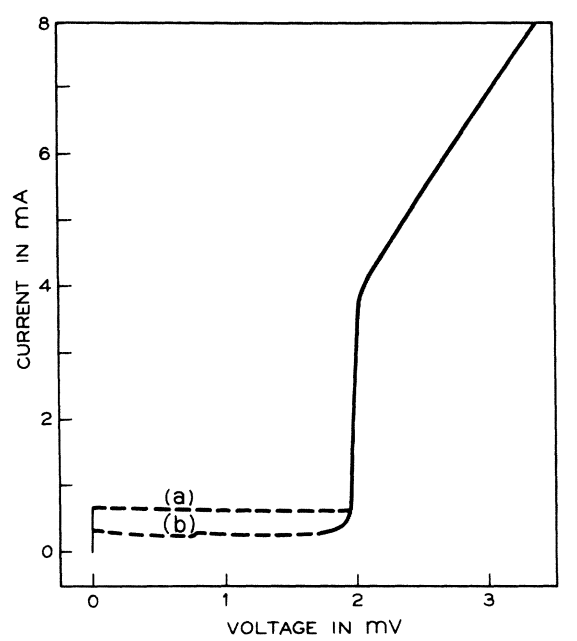
An I-V curve can also be seen at: Figure 12. "Electron microscope image of a Josephson junction its I-V curve".
I-V curve of the AC Josephson effect
. Source. Voltage is horizontal, current vertical. The vertical bar in the middle is the effect of interest: the current is going up and down very quickly between , the Josephson current of the device. Because it is too quick for the oscilloscope, we just see a solid vertical bar.
The non vertical curves at right and left are just other effects we are not interested in.
TODO what does it mean that there is no line at all near the central vertical line? What happens at those voltages?
Superconducting Transition of Josephson junction by Christina Wicker (2016)
Source. Amazing video that presumably shows the screen of a digital oscilloscope doing a voltage sweep as temperature is reduced and superconductivity is reached.If you shine microwave radiation on a Josephson junction, it produces a fixed average voltage that depends only on the frequency of the microwave. TODO how is that done more precisely? How to you produce and inject microwaves into the thing?
It acts therefore as a perfect frequency to voltage converter.
The Wiki page gives the formula: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Josephson_effect#The_inverse_AC_Josephson_effect You get several sinusoidal harmonics, so the output is not a perfect sine. But the infinite sum of the harmonics has a fixed average voltage value.
And en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Josephson_voltage_standard#Josephson_effect mentions that the effect is independent of the junction material, physical dimension or temperature.
All of the above, compounded with the fact that we are able to generate microwaves with extremely precise frequency with an atomic clock, makes this phenomenon perfect as a Volt standard, the Josephson voltage standard.
TODO understand how/why it works better.
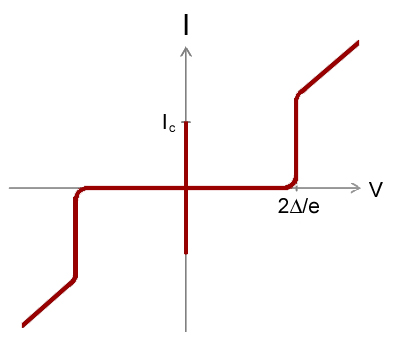
Two equations derived from first principles by Brian Josephson that characterize the device, somewhat like an I-V curve:where:
- : Josephson current
- : the Josephson phase, a function defined by the second equation plus initial conditions
- : input voltage of the system
- : current across the junction, determined by the input voltage
Note how these equations are not a typical I-V curve, as they are not an instantaneous dependency between voltage and current: the history of the voltage matters! Or in other words, the system has an internal state, represented by the Josephson phase at a given point in time.
To understand them better, it is important to look at some important cases separately:
- AC Josephson effect: V is a fixed DC voltage
Maximum current that can flow across a Josephson junction, as can be directly seen from the Josephson equations.
Is a fixed characteristic value of the physical construction of the junction.
A function defined by the second of the Josephson equations plus initial conditions.
It represents an internal state of the junction.
A device that exhibits the Josephson effect.
TODO is there any relationship between this and the Josephson effect?
Experimental observation published as Experimental Evidence for Quantized Flux in Superconducting Cylinders.
This appears to happen to any superconducting loop, because the superconducting wave function has to be continuous.
Video "Superconducting Qubit by NTT SCL (2015)" suggests that anything in between gets cancelled out by a superposition of current in both directions.
Paywalled at: journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.7.43
The first published experimental observation of the magnetic flux quantum.
The paper that follows it in the journal is also of interest, "Theoretical Considerations Concerning Quantized Magnetic Flux In Superconducting Cylinders" by N. Byers and C. N. Yang, it starts:So there was some previous confusion about the flux quantum due to the presence of Cooper pairs or not.
In a recent experiment, the magnetic flux through a superconducting ring has been found to be quantized in units of ch/2e. Quantization in twice this unit has been briefly discussed by London' and by Onsager. ' Onsager' has also considered the possibility of quantization in units ch/2e due to pairs of electrons forming quasi-bosons.
Dumping the fitures at: archive.org/details/experimental-evidence-for-quantized-flux-in-superconducting-cylinders One day we can also dump the paper scans when it goes into the public domain in 2056! Public domain scientific paper by year.
(Upper) Trapped flux in cylinder No. 1 as a function of magnetic field in which the cylinder was cooled below the superconducting transition. temperature. The open circles are individual data points. The solid circles represent th, e average value of all data points at a particular value of applied field including all the points plotted and additional data which could not be plotted due to severe overlapping of points. Approximately two hundred data points are represented. The lines are drawn at multiples of hc/2e.(Lower) Net flux in cylinder No. 1 before turning off the applied field in which it was cooled as a function of the applied field. Open and solid circles have the same significance as above. The lower line is the diamagnetic calibration to which all runs have been normalized. The other lines are translated vertically by successive steps of hc/2e.
(Upper) Trapped flux in cylinder No. 2 as a function of magnetic field in which the cylinder was cooled below the superconducting transition temperature. The circles and triangles indicate points for oppositely directed applied fields. Lines are drawn at multiples of hc/2e.(Lower) Net flux in cylinder No. 2 before turning off the applied field as a function of the applied field. The circles and triangles are points for oppositely directed applied fields. The lower line is the diamagnetic calibration to which all runs have The other been normalized. lines are translated vertically by successive steps of hc/2e.
The inverse of the magnetic flux quantum.
As mentioned in True Genius: The Life and Science of John Bardeen page 224, the idea of symmetry breaking was a major motivation in Josephson's study of the Josephson effect.
- the basis for the most promising 2019 quantum computing implementation: superconducting quantum computer
- Josephson voltage standard: the most practical/precise Volt standard, which motivated the definition of the ampere in the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units
- SQUID devices, which are:
- very precise magnetometer
- the basis for superconducting quantum computers
The most practical/precise volt standard.
It motivated the definition of the ampere in the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units
The wiki page en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Josephson_voltage_standard contains amazing schematics of the device, apparently made by the US Government.
Schematic of a typical Josephson voltage standard chip
. Source. Sam Benz demonstrating the equipment required the voltage standard
. Source. The evolution of voltage metrology to the latest generation of JVSs by Alain Rüfenacht
. Source. Talk given in 2023. The speaker is from NIST, and the talk was hosted by the BIPM. Fantastic talk.- youtu.be/VoRab8U2eS0?t=354 the desired output voltage is 10V
- youtu.be/VoRab8U2eS0?t=475 lists the three most commonly used 10V implementations currently:
Technical aspects of realizing the DC volt in the laboratory with a JVS by Stéphane Solve
. Source. Talk given in 2023. The speaker is from BIPM, and the talk was hosted by the BIPM. Fantastic talk.- youtu.be/6pgGNJby1lw?t=296 gives the experimental setup used to compare two different references. Notably it involves a nanovoltmeter
Can be used as a very precise magnetometer.
There are high temperature yttrium barium copper oxide ones that work on liquid nitrogen.
Superconducting Quantum Interference Device by Felipe Contipelli (2019)
Source. Good intuiotionistic video. Some points deserved a bit more detail.Mishmash of SQUID interviews and talks by Bartek Glowaki
. Source. The videos come from: www.ascg.msm.cam.ac.uk/lectures/. Vintage.
Mentions that the SQUID device is analogous to a double-slit experiment.
One of the segments is by John Clarke.
Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices by UNSW Physics (2020)
Source. An experimental lab video for COVID-19 lockdown. Thanks, COVID-19. Presented by a cute and awkward Adam Stewart.
Uses a SQUID device and control system made by STAR Cryoelectronics. We can see Mr. SQUID EB-03 written on the probe and control box, that is their educational product.
As mentioned on the Mr. SQUID specs, it is a high-temperature superconductor, so liquid nitrogen is used.
He then measures the I-V curve on an Agilent Technologies oscilloscope.
Unfortunately, the video doesn't explain very well what is happening behind the scenes, e.g. with a circuit diagram. That is the curse of university laboratory videos: some of them assume that students will have material from other internal sources.
- youtu.be/ql2Yo5LgU8M?t=211 shows the classic voltage oscillations, presumably on a magnetic field sweep, and then he puts a magnet next to the device from outside the Dewar
- youtu.be/ql2Yo5LgU8M?t=253 demonstrates the formation of Shapiro steps. Inserts a Rohde & Schwarz signal generator into the Dewar to vary the flux. The result is not amazing, but they are visible somewhat.
Tagged
Two parallel Josephson junctions.
In Ciro's ASCII art circuit diagram notation:
|
+-+-+
| |
X X
| |
+-+-+
|Specific type of Josephson junction. Probably can be made tiny and in huge numbers through photolithography.
Illustration of a thin-film superconducting tunnel junction (STJ)
Source. The superconducting material is light blue, the insulating tunnel barrier is black, and the substrate is green.Quantum Transport, Lecture 14: Josephson effects by Sergey Frolov (2013)
Source. youtu.be/-HUVGWTfaSI?t=878 mentions maskless electron beam lithography being used to produce STJs.Alfred Leitner - Liquid Helium II the Superfluid by Alfred Leitner (1963)
Source. Original source: www.alfredleitner.com.Ben Miller experiments with superfluid helium by BBC (2011)
Source. Just quickly shows the superfluid helium climbing out o the cup, no detailed setup. With professor Robert Taylor from the University of Oxford.Something weird happens when you keep squeezing by Vox (2023)
Source. Sodium becomes liquid when you compress it. Weird. Tagged
Inward Bound by Abraham Pais (1988) page 282 shows how this can be generalized from the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
Tagged
TODO WTF is this? How is it built? What is special about it?
Mentioned a lot in the context of superconducting quantum computers, e.g. youtu.be/t5nxusm_Umk?t=268 from Video "Quantum Computing with Superconducting Qubits by Alexandre Blais (2012)",
Mentioned at: Video "Quantum Computing with Light by Quantum Light University of Sheffield (2015)" youtu.be/nyK-vhoOBpE?t=185.
Tagged
Tagged
www.youtube.com/watch?v=PbuiIhr0LVA 7 Different Types of Plastic and Their Uses by Orange Plastics Academy (2018) Does not mention packaging foams.
Signup required for any search, bastards. But it's free. Once you have a URL however it is visible without login, so you could just Google it too.
Variation of saturation magnetisation with temperature for Nickel
. Source. This graph shows what happens when you approach the Curie temperature from below.The wiki comments: en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Ferromagnetism&oldid=965600553#Explanation
The Bohr-van Leeuwen theorem, discovered in the 1910s, showed that classical physics theories are unable to account for any form of magnetism, including ferromagnetism. Magnetism is now regarded as a purely quantum mechanical effect. Ferromagnetism arises due to two effects from quantum mechanics: spin and the Pauli exclusion principle.
To understand the graph, first learn/remember the difference between the magnetic B and H field.
The interest of the magnetic hysteresis graph is that it serves as an important characterization of a :This curve will also tell you how many turns of the coil will be needed to reach the required field.
- its area gives you the hysteresis loss of the transformer, which is a major cause of efficiency loss of the component
- some key points of the curve give important characterizations of the core/material:
- Saturation magnetisation
- magnetization strength without field
- how much field you need to demagnetize it
Theoretical magnetic hysteresis plot
. Source. Measurement of B-H characteristic
. Source. 1989. 1989 and they were making such awesome materials. It is hard to understand why university still exists given this.
Shows how you can obtain the magnetic hysteresis curve with an AC source plus an oscilloscope in XY mode. youtu.be/pXukVix5Pcw?t=193 clearly shows the measurement circuit.
Magnetic hysteresis experiment by UNSW Physics.
Source. 2020, thanks COVID-19. Like other UNSW Physics YouTube channel videos, the experimental setup could be made clearer with diagrams.
But this video does have one merit: it shows that the hysteresis plot can be obtained directly with the oscilloscope XY mode by using an AC source. The Y axis is just a measure of the total magnetic field induced by the primary coil + the magnetization of the material itself.
Electromagnets allow us to create controllable magnetic fields, i.e.: they act as magnets that we can turn on and off as we please but controlling an input voltage.
Compare them to permanent magnet: on a magnet, you always have a fixed generated magnetic field. But with an electromagnet you can control the field, and even turn it off entirely.
This type of "useful looking thing that can be controlled by a voltage" tends to be of huge importance in electrical engineering, the transistor being another example.
Solenoid means "tubular" in Greek.
Solenoids are simpler to build as they don't require insulated wire as in modern electrical cable because as the electromagnetic coils don't touch one another.
As such it is perhaps the reason why some early electromagnetism experiments were carried out with solenoids, which André-Marie Ampère named in 1823.
But the downside of this is that the magnetic field they can generate is less strong.
Illustration of a solenoid
. Magnetic field lines around a solenoid cross-section
. TODO accurate simulation or not?Easy-to-Build Electromagnet lifts over 50 lbs by Dorian McIntire
. Source. Fun, but zero reproducibility.Is it realistic?
Yeah, bitch! Magnets! scene from Breaking Bad
. Source. Police evidence magnet scene from Breaking Bad
. Source. Toy model of matter that exhibits phase transition in dimension 2 and greater. It does not provide numerically exact results by itself, but can serve as a tool to theorize existing and new phase transitions.
Each point in the lattice has two possible states: TODO insert image.
As mentioned at: stanford.edu/~jeffjar/statmech/intro4.html some systems which can be seen as modelled by it include:
- the spins direction (up or down) of atoms in a magnet, which can undergo phase transitions depending on temperature as that characterized by the Curie temperature and an externally applied magnetic fieldNeighboring spins like to align, which lowers the total system energy.
- the type of atom at a lattice point in a 2-metal alloy, e.g. Fe-C (e.g. steel). TODO: intuition for the neighbor interaction? What likes to be with what? And aren't different phases in different crystal structures?
Also has some funky relations to renormalization TODO.
Bibliography:
The Ising Model in Python by Mr. P Solver
. Source. The dude is crushing it on a Jupyter Notebook.TODO what it means to solve an Ising model in general?
stanford.edu/~jeffjar/statmech/lec4.html gives some good notions:
- is the expectation value of the value. It is therefore a number between -1.0 an and 1.0, -1.0 means everything is always down, 0.0 means half up half down, and 1.0 means all up
- : correlation between neighboring states. TODO.
A tiny idealized magnet! It is a very good model if you have a small strong magnet interacting with objects that are far away, notably other magnetic dipoles or a constant magnetic field.
The cool thing about this model is that we have simple explicit formulas for the magnetic field it produces, and for how this little magnet is affected by a magnetic field or by another magnetic dipole.
This is the perfect model for electron spin, but it can also be representative of macroscopic systems in the right circumstances.
The intuition for the name is likely that "dipole" means "both poles are on the same spot".
Different macroscopic magnets can be approximated by a magnetic dipole when shrunk seen from far away
. Source. We define a "water compass" as a compass made by placing a magnet floating on a water surface to reduce friction and allow it to align with the Earth's magnetic field. This is a common children's scientific experiment.
Applications: produce high magnetic fields forAs of the early 2020s, superconducting magnets predominantly use low temperature superconductors Nb-Ti and Nb-Sn, see also most important superconductor materials, but there were efforts underway to create practical high-temperature superconductor-based magnets as well: Section "High temperature superconductor superconducting magnet".
- magnetic resonance imaging, the most important commercial application as of the early 2020s
- more researchy applications as of the early 2020s:
Wikipedia has done well for once:
The current to the coil windings is provided by a high current, very low voltage DC power supply, since in steady state the only voltage across the magnet is due to the resistance of the feeder wires. Any change to the current through the magnet must be done very slowly, first because electrically the magnet is a large inductor and an abrupt current change will result in a large voltage spike across the windings, and more importantly because fast changes in current can cause eddy currents and mechanical stresses in the windings that can precipitate a quench (see below). So the power supply is usually microprocessor-controlled, programmed to accomplish current changes gradually, in gentle ramps. It usually takes several minutes to energize or de-energize a laboratory-sized magnet.
Superconductivity: magnetic separation by University of Cambridge
. Source. They are pioneers in making superconducting magnets, physicist from the university taking obsolete equipment from the uni to his garage and making a startup kind of situation. This was particularly notable for this time and place.
They became a major supplier for magnetic resonance imaging applications.
Used to explain the black-body radiation experiment.
Published as: On the Theory of the Energy Distribution Law of the Normal Spectrum by Max Planck (1900).
The Quantum Story by Jim Baggott (2011) page 9 mentions that Planck apparently immediately recognized that Planck constant was a new fundamental physical constant, and could have potential applications in the definition of the system of units (TODO where was that published):This was a visionary insight, and was finally realized in the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units.
Planck wrote that the constants offered: 'the possibility of establishing units of length, mass, time and temperature which are independent of specific bodies or materials and which necessarily maintain their meaning for all time and for all civilizations, even those which are extraterrestrial and nonhuman, constants which therefore can be called "fundamental physical units of measurement".'
TODO how can it be derived from theoretical principles alone? There is one derivation at; en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planck%27s_law#Derivation but it does not seem to mention the Schrödinger equation at all.
Quantum Mechanics 2 - Photons by ViaScience (2012)
Source. Contains a good explanation of how discretization + energy increases with frequency explains the black-body radiation experiment curve: you need more and more energy for small wavelengths, each time higher above the average energy available.Derived from classical first principles, matches Planck's law for low frequencies, but diverges at higher frequencies.
- The Quantum Story by Jim Baggott (2011) page 10 mentions:and the footnote comments:
Early examples of such cavities included rather expensive closed cylinders made from porcelain and platinum.
The study of cavity radiation was not just about establishing theoretical principles, however. It was also of interest to the German Bureau of Standards as a reference for rating electric lamps.
- 1859-60 Gustav Kirchhoff demonstrated that the ratio of emitted to absorbed energy depends only on the frequency of the radiation and the temperature inside the cavity
- 1896 Wien approximation seems to explain existing curves well
- 1900 expriments by Otto Lummer and Ernst Pringsheim show Wien approximation is bad for lower frequencies
- 1900-10-07 Heinrich Rubens visits Planck in Planck's villa in the Berlin suburb of Grünewald and informs him about new experimental he and Ferdinand Kurlbaum obtained, still showing that Wien approximation is bad
- 1900 Planck's law matches Lummer and Pringsheim's experiments well. Planck forced to make the "desperate" postulate that energy is exchanged in quantized lumps. Not clear that light itself is quantized however, he thinks it might be something to do with allowed vibration modes of the atoms of the cavity rather.
- 1900 Rayleigh-Jeans law derived from classical first principles matches Planck's law for low frequencies, but diverges at higher frequencies.
Black-body Radiation Experiment by sciencesolution (2008)
Source. A modern version of the experiment with a PASCO scientific EX-9920 setup.What is the Ultraviolet Catastrophe? by Physics Explained (2020)
Source. Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting (TCSPC) with the Fluorolog Fluorimeter by Yale CBIC (2011)
Source. One important quantum mechanics experiment, which using quantum effects explain the dependency of specific heat capacity on temperature, an effect which is not present in the Dulong-Petit law.
This is the solid-state analogue to the black-body radiation problem. It is also therefore a quantum mechanics-specific phenomenon.
Observation that all solids appear to have the same constant heat capacity per mole.
It can be seen as the limit case of an Einstein solid at high temperatures. At lower temperatures, the heat capacity depends on temperature.
Wikipedia mentions that it is completely analogous to Planck's law.
What makes lasers so special: Lasers vs other light sources.
How Lasers Work by Scientized (2017)
Source. An extremely good overview of how lasers work. Clearly explains the electron/photon exchange processes involved, notably spontaneous emission.
Talks about the importance of the metastable state to achieve population inversion.
Also briefly explains the imperfections that lead to the slightly imperfect non punctual spectrum seen in a real laser.
- youtu.be/_JOchLyNO_w?t=188 says LED is "also monochromatic", but that is not strictly true, it has way way larger frequency band than a laser. Only narrower compared to other sources such as incandescent light bulbs.
- youtu.be/_JOchLyNO_w?t=517 stimulated emission. This is the key to laser formation as it produces coherent photons.
- youtu.be/_JOchLyNO_w?t=581 spontaneous emission happens too fast (100 ns), which is not enough time for stimulated emission to happen. Metastable electrons to the rescue.
- youtu.be/_JOchLyNO_w?t=832 the parallel mirrors select perpendicular photons preferentially
Laser Fundamentals I by Shaoul Ezekiel
. Source. 2008, MIT. Many more great videos in this series.Bibliography:
Tagged
Spectrum of laser light by Shaoul Ezekiel
. Source. 2008, MIT. Tagged
Laser linewidth - measurement and explanation by Your Favourite TA
. Source. TODO why it exists:
The key advantages of lasers over other light sources are:
- lasers emit a narrow spectrum
- it can be efficient collimated, while still emitting a lot of output power: Section "Why can't you collimate incoherent light as well as a laser?"
- can be phase and polarization coherent, though it is not always the case? TODO.
One cool thing about lasers is that they rely on one specific atomic energy level transition to produce light. This is why they are able to to be so monchromatic. Compare this to:As such, lasers manage to largely overcome "temperature distribution-like" effects that create wider wave spectrum
- incandescent bulbs: wide black-body radiation spectrum
- LED: has a wider spectrum fundamentally related to an energy distribution, related: Why aren't LEDs monochromatic
- TODO think a bit about fluorescent lamps. These also rely on atomic energy transitions, but many of them are present at once, which makes the spectrum very noisy. But would individual lines be very narrow?
It emits a very narrow range of frequencies (small linewidth), which for many purposes can be considered a single frequency.
It does however have a small range of frequencies. The smaller the range, the better the laser quality.
electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/477264/spectrum-of-leds claims cheap LEDs have 20 nm width at 50% from peak, and cheap lasers can be 1 nm or much less
You could put an LED in a cavity with a thin long hole but then, most rays, which are not aligned with the hole, will just bounce inside forever producing heat.
So you would have a very hot device, and very little efficiency on the light output. This heat might also behave like a black-body radiation source, so you would not have a single frequency.
The beauty of lasers is the laser cavity (two parallel mirrors around the medium) selects parallel motion preferentially, see e.g.: youtu.be/_JOchLyNO_w?t=832 from Video 31. "How Lasers Work by Scientized (2017)"
Closely related to optical amplifiers.
This is by far the most important type of laser commercially, as it can be made relatively cheaply, and it doesn't break easily as it ends up being a single crystal.
Compare them for example to the earlier gas lasers.
This is the type of laser that you would get in a simple laser pointer.
But the real mega aplications are:
- fiber-optic communication, where laser diodes are one of the most commonly used methods to generate the light that goes in the fiber. This makes laser diodes one of the most important inventions of the 20th centure without doubt.
- optical storage. But as of the 2020s its usefulness was much diminished by a combination of solid-state storage + faster Internet due largely to fiber-optic communication. So it is partly a matter of laser diodes beating laser diodes!
The type of laser described at: Video 31. "How Lasers Work by Scientized (2017)", notably youtu.be/_JOchLyNO_w?t=581. Mentioned at: youtu.be/_JOchLyNO_w?t=759 That point also mentions that 4-level lasers also exist and are more efficient. TODO dominance? Alternatives?
Three-level laser system by Dr. Nissar Ahmad (2021)
Source. Bibliography:
Sample usages:
- quantum computing startup Atom Computing uses them to hold dozens of individual atoms midair separately, to later entangle their nuclei
Optical Tweezers Experiment by Alexis Bishop
. Source. Setup on a optical table. He drags a 1 micron ball of polystyrene immersed in water around with the laser. You look through the microscope and move the stage. Brownian motion is also clearly visible when the laster is not holding the ball. Tagged
The opposite of elementary particle.
As a phisicist once amazingly put it in a talk Ciro watched:
It all depends on how much energy you have to probe nature with. Previously, we thought protons were elementary particles. But then we used more energy and found that they aren't.If some alien race had even less energy, they might not know about electrons at all, and could think that anyons are actually elementary.Being an "elementary particle" is always a possibly temporary label.
Bibliography:
Bibliography:
- When condensed matter physics became king by Joseph D. Martin (2019): physicstoday.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/PT.3.4110
- www.youtube.com/watch?v=RImqF8z91fU&list=PLtTPtV8SRcxi91n9Mni2xcQX4KhjX91xp Solid State Physics" course by Sergey Frolov taught at the University of Pittsburgh in the Fall 2015 semester
Tagged
Affiliation: University of São Paulo.
 Ciro Santilli
Ciro Santilli OurBigBook.com
OurBigBook.com